
Map unknown devices to switch portsįor those IPs that you couldn't map to known devices, the commands in the previous section will tell you which port you need to check.
Show mac address table traffic curent for mac#
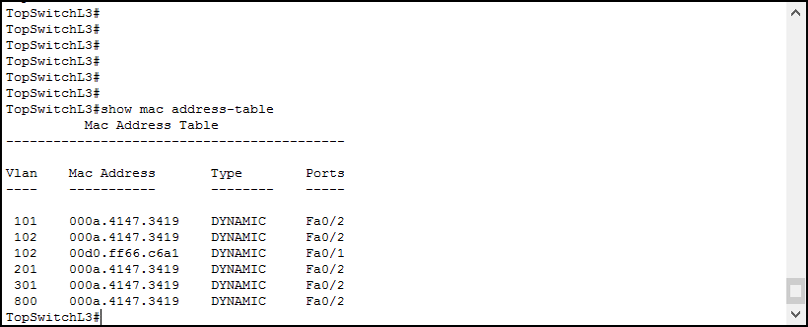
Note, the default time out for MAC address tables on Cisco devices is 5 minutes you may need to run your broadcast ping again in order to repopulate it. Will show you the MAC address table for all ports in that VLAN. Alternatively: show mac-address-table vlan Will show you the MAC address table entry for that particular MAC, including which switch port it's connected to. Take the list of MAC addresses and use it to determine which switch port each device is connected to. Any IP address that you can't match a name to should be flagged for further investigation. You can check the list of IPs against DNS (or another naming service) to identify the names of specific devices.
This will give you all the IPs and MAC addresses of every device that responded to the ping. This will populate the ARP cache of the router with entries for all machines on each subnet responding to ping.Īgain on the first hop routers, extract the list of ARP entries for each subnet: show ip arp interface vlan 100 Note, this should be the directed broadcast address of each subnet, rather than the 'all devices' broadcast IP of 255.255.255.255 In Cisco IOS, this can only be done from privileged exec mode.

My suggestions for this (assuming Cisco managed routers/switches): Identify known devicesįrom your first hop router(s), do a broadcast ping on each subnet that is trunked to a switch supporting the office space (as opposed to any data centre space you may have). In this case, it sounds like the best option is to identify all switch ports that are connected to devices you know about. Not quite a dupe, but there's a similar question here, which has some suggestions about mapping an IP address to a switch port. I guess my question is as above, is there a way to display the IP or name of whatever is attached to that port on the switch?
Show mac address table traffic curent Pc#
Is there a way, either by IP or name, to query a Cisco switch to tell you which port# that particular PC is plugged into?Ģ) There are a few ports on the switches which are lit up, indicating activity, but when I trace them back to the relay rack, they are attached to ports which are no longer in use, or no longer exist. But, it most definitely is active and on the network. Problem is, the port that it's plugged into on the switch, is not lit up, showing it as inactive. So I go to the relay rack, find port 28, and trace it to the switch.

For example, there is a logged in laptop plugged into jack# 28. Today, I'm recreating a spreadsheet which lists all of our current physical network jacks, and where they are located in the resized office.ġ) A few of the network jack numbers don't seem to be syncing up with the labels on the relay racks. Prior to us closing it off, I jotted down the network jack #'s on the side to be closed and made sure to disconnect them from the switches in our server room. We gave back the unused space to the building management and had it walled off. To calculate the total Interference Index for a channel add “a+b+c+d”.Our company recently closed down half our office space, which was not being used. Metric value “d” is the interference the AP’s neighbors see on the adjacent channel Metric value “c” is the channel interference the AP’s neighbors see on the selected channel. Metric value “b” is the interference the AP sees on the adjacent channel. Metric value “a” is the channel interference the AP sees on its selected channel. The Interference Index is calculated as a/b//c/d, where: The AP uses this metric to measure co-channel and adjacent channel interference. The coverage index is calculated as x/y, where “x” is the AP’s weighted calculation of the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) on all valid APs on a specified 802.11 channel, and “y” is the weighted calculation of the Aruba APs SNR the neighboring APs see on that channel. The AP uses this metric to measure RF coverage. The number of non-unicast frames sent on the channel. Number of frames sent at a data rate of 18 Mbps or slower. Number of 802.11 retry frames sent because a client failed to send an ACK. Number of a radio channel used by the AP. The output of this command includes the following information: The output of this command shows ARM neighbor information for both the wifi1 and wifi0 interfaces on AP ap70_1.
Enter the IP address in dotted-decimal format. Show data for an AP with a specific IP address. An AP’s BSSID is usually the AP’s MAC address. Show data for a specific Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID). Show data for an AP with a specific name. Show the ARM settings for an AP’s neighbors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
